
What is Low Carbon Aviation Fuel (SAF)?








Low Carbon Aviation Fuel (SAF)
Produced from feedstocks such as inedible waste fats and oils, high lipid oil crops, municipal green bin waste, rubber tires or recycled plastic waste.
vs.








Existing Aviation Fuel
Produced by refining fossil fuels extracted from the earth resulting in a negative effect on the environment as they release carbon from the past.








Low Carbon Aviation Fuel (SAF)
Produced from feedstocks such as inedible waste fats and oils, high lipid oil crops, municipal green bin waste or rubber tires or recycled plastic waste.
vs.








Existing Aviation Fuel
Produced by refining fossil fuels extracted from the earth resulting in a negative effect on the environment as they release carbon from the past.








OUR PRODUCTS:
Select Fuel is working with partners to produce many forms of fuel, at scale, for ALL Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) power-plants.
4 types of Biofuel we are producing from recycled waste:


LOW CARBON AVIATION FUEL OR SAF
- SAF has similar properties to conventional jet fuel but with a smaller carbon footprint


BIOFUEL for VEHICLES
- Racing Fuel
- Passenger Vehicle Fuel


BIO DIESEL
- Converting plastic into diesel fuel

CONDENSATE
- Condensate is used to dilute highly viscous, heavier oils that cannot otherwise be transported via pipelines.








BENEFITS OF USING LOW CARBON AVIATION FUEL (SAF)


When fossil fuels are used to provide energy, they release carbon from the past, resulting in a net increase of CO2 in the atmosphere.
When Low Carbon Aviation Fuel combusts in an aircraft engine, the resulting CO2 emissions are returning carbon to the atmosphere.
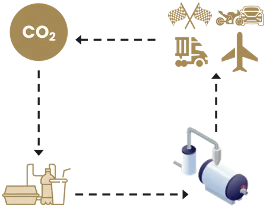

From a life-cycle perspective, there is
NO net addition of CO2 to the atmosphere from Low Carbon Aviation Fuel combustion.

